External Input
In the xronos framework, Ports and Connections are the primary mechanism for sending and receiving data. However, often programs also have to read input from components that are not directly controlled by the framework. For instance, a program might want to receive input from a file, from the console, or from a socket. For this, the xronos framework provides a set of library reactors that allow receiving input from an external data sources. They assign a timestamp to any data received and forward the data using an output port. Currently, the following library reactors are provided for reading external input.
Note
While it is possible to use blocking reads in reaction handlers
(e.g., input(...)), this is discouraged as it potentially
blocks the entire program and no other reactions are executed in the meantime.
Using the library input reactors ensures that blocking reads do not affect
the overall program execution.
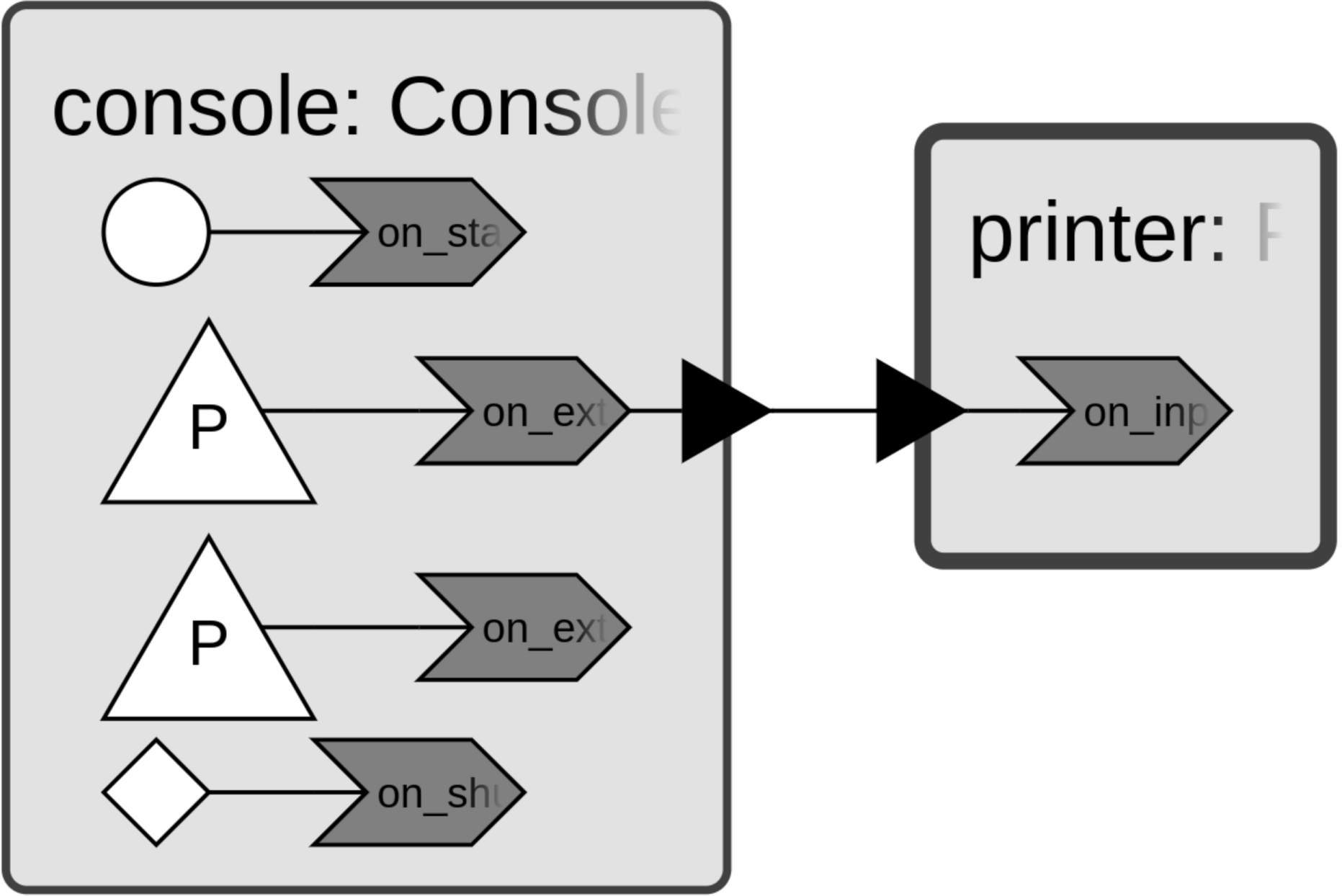
Reading from Console
The ConsoleInput can be used to read data from the console.
Consider the following example program.
import xronos
import xronos.lib
class Printer(xronos.Reactor):
input_ = xronos.InputPortDeclaration()
@xronos.reaction
def on_input(self, interface):
input_trigger = interface.add_trigger(self.input_)
return lambda: print(input_trigger.get())
def parser(x):
if x in {"exit", "quit"}:
raise xronos.lib.ConsoleInput.RequestShutdown
return x
def main():
env = xronos.Environment()
printer = env.create_reactor("printer", Printer)
console = env.create_reactor("console", xronos.lib.ConsoleInput, parser)
env.connect(console.output, printer.input_)
env.execute()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
from typing import Callable
import xronos
import xronos.lib
class Printer(xronos.Reactor):
input_ = xronos.InputPortDeclaration[str]()
@xronos.reaction
def on_input(self, interface: xronos.ReactionInterface) -> Callable[[], None]:
input_trigger = interface.add_trigger(self.input_)
return lambda: print(input_trigger.get())
def parser(x: str) -> str:
if x in {"exit", "quit"}:
raise xronos.lib.ConsoleInput.RequestShutdown
return x
def main() -> None:
env = xronos.Environment()
printer = env.create_reactor("printer", Printer)
console = env.create_reactor("console", xronos.lib.ConsoleInput[str], parser)
env.connect(console.output, printer.input_)
env.execute()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
This program defines a simple Printer reactor that prints any strings that it
receives on its input port. The main() function instantiates the Printer
reactor and connects its input to an instance of
ConsoleInput. The custom parser function that is provided
as an argument simply forwards all received strings. However, if a string equals
“quit” or “exit”, then it raises a
RequestShutdown exception to instruct the
console input reactor to stop reading input and terminate the program.
When executing the program, it immediately echos any lines entered by the user and terminates if the user types “quit” or “exit”.
$ python console.py
> test
> test
exit
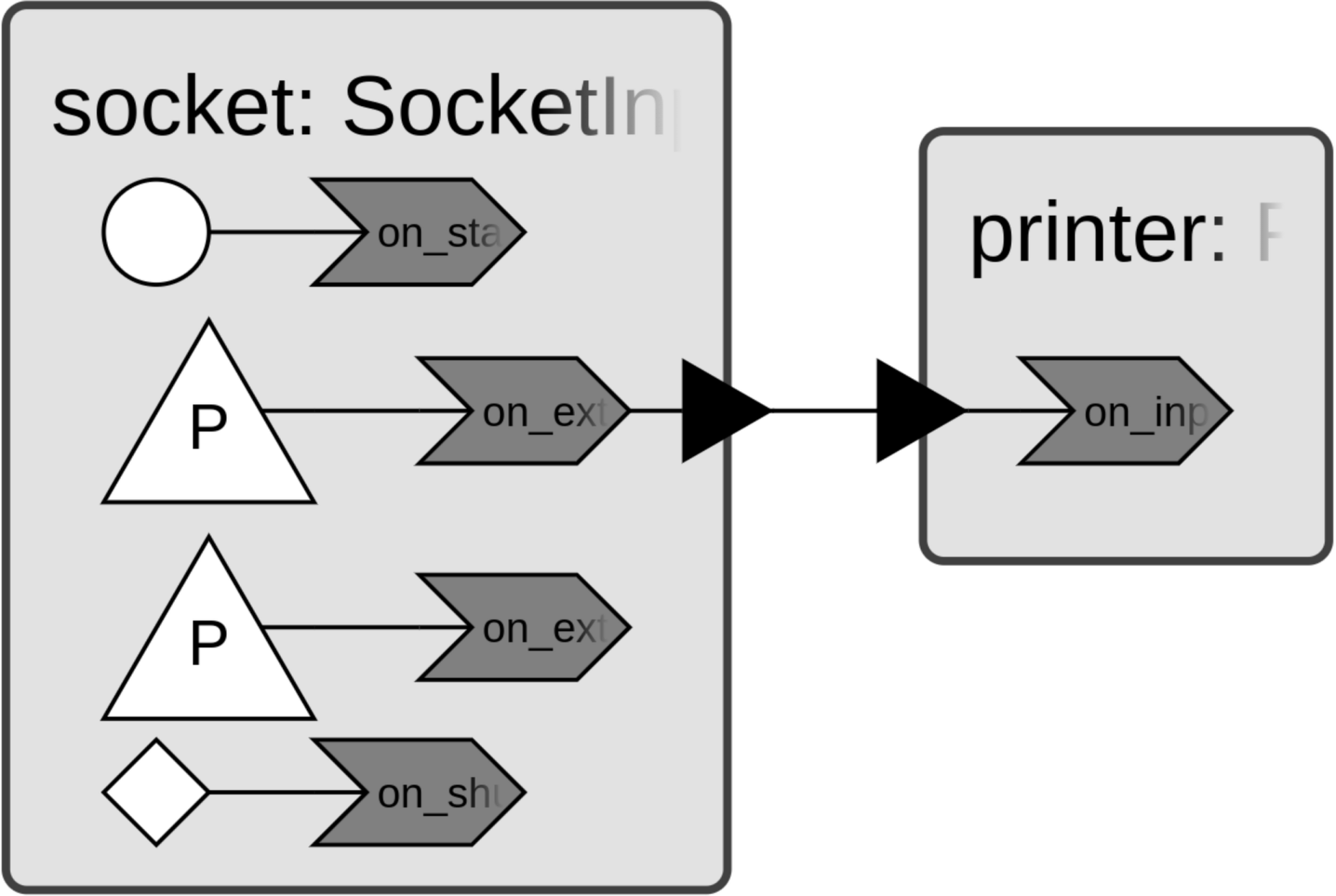
Reading from a Socket
The InputSocket reactor allows receiving data from a
socket. Consider the following example program.
import xronos
import xronos.lib
class Printer(xronos.Reactor):
input_ = xronos.InputPortDeclaration()
@xronos.reaction
def on_input(self, interface):
input_trigger = interface.add_trigger(self.input_)
return lambda: print(input_trigger.get().decode("utf-8"))
def main():
env = xronos.Environment()
printer = env.create_reactor("printer", Printer)
socket = env.create_reactor(
"socket",
xronos.lib.SocketInput,
host="localhost",
port=1234,
mode=xronos.lib.SocketInput.Mode.TCP_SERVER,
)
env.connect(socket.output, printer.input_)
env.execute()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
from typing import Callable
import xronos
import xronos.lib
class Printer(xronos.Reactor):
input_ = xronos.InputPortDeclaration[bytes]()
@xronos.reaction
def on_input(self, interface: xronos.ReactionInterface) -> Callable[[], None]:
input_trigger = interface.add_trigger(self.input_)
return lambda: print(input_trigger.get().decode("utf-8"))
def main() -> None:
env = xronos.Environment()
printer = env.create_reactor("printer", Printer)
socket = env.create_reactor(
"socket",
xronos.lib.SocketInput,
host="localhost",
port=1234,
mode=xronos.lib.SocketInput.Mode.TCP_SERVER,
)
env.connect(socket.output, printer.input_)
env.execute()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
This instantiates the InputSocket reactor in TCP server
mode listening on port 1234 of localhost. Any data received on the socket will
be printed by the Printer reactor.
Try running the program and then open
http://loalhost:1234 in your browser. This should
produce output similar to the following:
$ python socket.py
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:1234
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:134.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/134.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br, zstd
DNT: 1
Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
Sec-Fetch-Dest: document
Sec-Fetch-Mode: navigate
Sec-Fetch-Site: none
Sec-Fetch-User: ?1
Priority: u=0, i
Other Input
ExternalInput is a generic reactor that can be used to read
input from arbitrary other sources. It is configured with an arbitrary
generator. The
generator is expected to yield received values. Any value yielded from the
generator will be timestamped and forwarded to the output port. See
ExternalInput for usage instructions and an example
generator function.